As soon as the health benefits of the Mediterranean diet were substantiated, people began to recognize the undeniable connection between food and well-being. Regrettably, the predominant focus on promoting a single food item within this dietary regimen overlooks the fact that even so-called superfoods cannot provide all the essential nutrients and health advantages of a well-rounded diet.
Today at Bright Side, we have delved into the potential consequences of overindulging in nutritious foods.
1. Carrots

Carrots contain a high amount of beta-carotene, which the body converts into vitamin A. There is no risk of excess vitamin A because the body regulates the conversion of beta-carotene as needed. However, having an excess of beta-carotene in the body can lead to carotenemia, a condition that causes a yellowish discoloration of the skin. This discoloration gradually disappears as the excess carotene is metabolized and poses no harm.
2. Kombucha
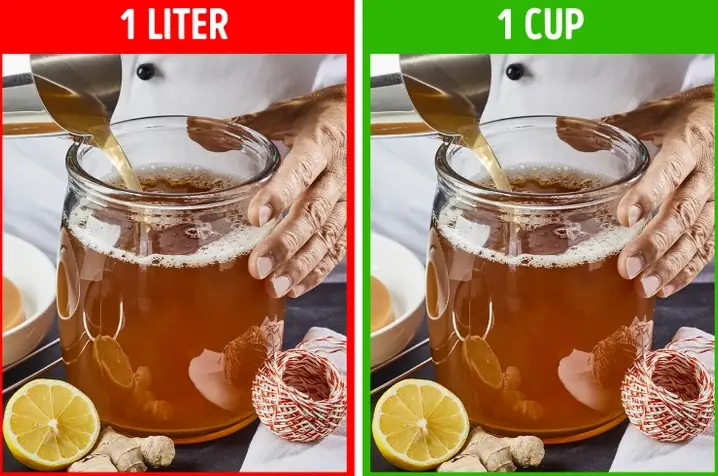

3. Water

Excessive water intake can lead to an electrolyte imbalance, as it can cause a significant reduction in sodium levels when the kidneys are unable to process it effectively. In severe cases, this can result in the accumulation of water in the brain, leading to swelling and increased pressure, as the human skull is unable to expand. Although rare, these scenarios have been observed in athletes who feel a compulsive urge to rehydrate after rigorous training sessions and in individuals with kidney issues.
4. Avocado
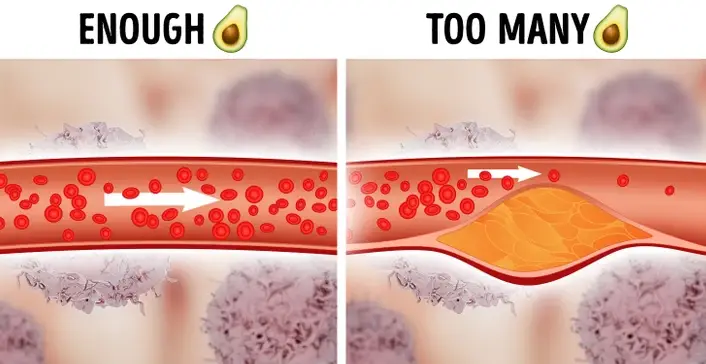
Avocados are rich in fiber and packed with essential vitamins, offering benefits like lowering bad cholesterol (LDL) and supporting cellular health because of their high monounsaturated fat content. However, it’s important to note that fat is still energy-dense. With around 240 calories in a single avocado, representing about 10%-20% of an individual’s recommended daily intake, overconsumption can lead to health issues, especially related to artery health. It’s advisable to stick to half or a whole avocado per day when consumed in their natural, raw state.
5. Beetroot

6. Seaweed

7. Soy and its derivatives

Soy-based foods are abundant in essential nutrients like vitamin B, fiber, potassium, magnesium, and high-quality protein. They are acknowledged as a complete protein source as they encompass all 9 essential amino acids that the body requires but cannot produce on its own. However, if you have adjusted your diet recently due to thyroid issues, be cautious: soy could potentially hinder the effectiveness of hormone medication utilized to manage hypothyroidism in women. While research findings are inconclusive, it’s prudent to closely monitor this situation.
8. Chia seeds

Despite the prevalence of chia seeds being touted as a superfood due to their rich omega-3 content, there is currently little valid proof backing their health advantages, particularly concerning cardiovascular disease. The omega-3 found in chia seeds is not as easily absorbed as that found in salmon. As a result, despite the elevated content, consuming approximately 100 grams of chia seeds would be necessary to absorb the same amount as from fish. The dilemma? 100 grams of chia seeds equate to roughly 500 calories, akin to the calorie count of a fast-food hamburger.
Is it truly advantageous for one’s health to excessively consume any type of food? Why do individuals tend to overindulge in these so-called ‘healthy’ foods? Share your thoughts in the comments section!





Leave a Comment